| |
KeyTropin
Studies
Recombinant Growth
Hormone Stimulator and its effect on LPL in rats and humans.
ABSTRACT
The
decline activity of the growth hormone Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)
axis with advancing age may contribute to the decrease in lean body mass
and the increase in mass of adipose tissue that occurs with aging.
Growth hormone (GH) has profound effect
on lipid metabolism. Body fat mass and lipoprotein metabolism are regulated
by GH. Lipoprotein - Lipase (LPL) is a key enzyme of triglyceride removal
from the circulation, and hence, supply adipose as well as muscle tissue
with fatty acids for storage or as an energy fuel. In the present study,
the regulation of GH receptor (GHR) and the GH dependent growth factor,
IGF-1, expression by recombinant GH Stimulator in an adipose tissue of
hypophysectionized rats was investigated.
Effects
of recombinant GH Stimulator in the regulation of LPL activity in an adipose
tissue and muscle tissue were studied to get future insight into the mechanism
by which GH and IGF-1 regulate body fat and lipoprotein metabolism.
After a single injection of recombinant GH Stimulator,
GHR-mRNA was induced in two hours. A GH dose dependent increase in GHR-mRNA
level was found. Northern blot analysis revealed two transcripts of 3.6
Kb and of 1.2 Kb, which are believed to have encoded the full length GH
receptor and a GH binding protein, respectively. GH-treatment dose dependently
increased IGF-1 mRNA level.
To
test this result in vivo (see study below), we studied IGF-1 plasma with
20 healthy men from 40 - 78 years old who had plasma IGF-1 concentration
of less than 350 units per liter, six months base line time period and
a six month treatment period that followed.
During treatment period, Group 1 received .02mg
of recombinant GH Stimulator. Group 2 received no treatment.
Results:
Group 1 - the mean plasma IGF-1 level rose from 500 to 1000 units per
liter during treatment (teen age level) - 8% increase in lean body mass,
14% decrease in adipose tissue, and 0.1% increase in skin thickness. Group
2 - No change in body mass, skin thickness, or bone density.
Conclusion:
Decrease in secretion of hGH is responsible in part for the decrease of
lean body mass, the expansion of adipose
tissue mass, and the thinning of the skin that occurs in old age.
INVESTIGATIVE CLINICAL
TRIAL: KeyTropin with HTA5 (referred to above)
KeyTropin™
is a 100% natural, orally administered human growth hormone (hGH) releasing
complex in the form of HTA5
(patent pending) that is supplemented with natural amino acids to assist
in your body's own release of hGH.
The
fundamental "key" to the KeyTropin complex is the presence of a small
amino acid complex, HTA5. HTA5
acts like your body's own releasing factor to stimulate the release of
hGH. However, by including the amino acids Iysine and arginine into a
mixture with HTA5, it was discovered that the
activity of HTA5, was potentiated. The end
result was a much higher concentration of released hGH than either amino
acids or HTA5 alone could be expected to produce.
Over
the past decade, our understanding of the role of hGH has expanded tremendously.
It has been found that hGH is not only responsible for the increase in
the body's physical size, for which it was initially named. Indeed, circulating
hGH has been shown to positively influence the immune response, our sleep
cycle, glucose metabolism, cholesterol synthesis, our body composition,
cardiac function, and even sexual activity, just to name a few. Unfortunately,
the concentration of hGH drops precipitously with age, as do the benefits
that it may provide to maintain vitality.
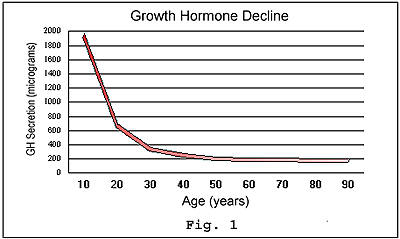
Given
these findings, the term Growth Hormone Deficiency Syndrome was coined
to describe the changes in our bodies' physiology that occur with the
decrease in hGH after somatic growth (i.e., growth in body size) has finished
in the our early 20's. The long-term hope, of course, was that with time
researchers would develop a method to safely supplement hGH in adults.
The evolution of hGH supplementation, from injectable preparations to
a new class of orally administered sprays that stimulate the release of
hGH, have fulfilled the promise of maintaining vitality and countering
the aging process. Of course, the major question with the development
of this new technology is simply this: Can the oral administration of
an hGH releasing stimulant produce a significant physiological, effect?
Two
trials were conducted, one to prove the efficacy of HTA5
and one to determine if combining it with the amino acids lysine and arginine
could increase IGF-1 levels in excess of HTA5
alone.
In
trial #1, ten individuals ranging in age from 30 to 69 years were given
30 nanograms (ng) of HTA5 in the form of an
aerosolized oral spray before bed, over a 32 period. Results confirmed
that HTA5, by itself, is a bona fide, standalone GH releasing factor.
In
trial #2, fifteen individuals ranging in age from 38 to 70 years of age
were given an effervescent tablet containing 20 nanograms (ng.) of HTA5
in combination with 1200 mg. each of the amino acids lysine and arginine.
The study participants took the tablet daily before bed for a period of
36 days. Blood tests were conducted on each participant at the beginning
of the study and at its conclusion to create a collection of data which
illustrates the considerable efficacy of HTA5.
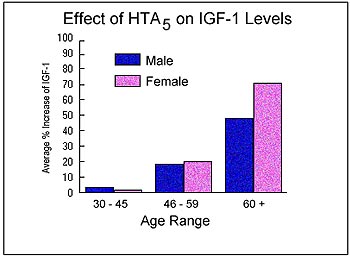
Since
growth hormone acts primarily through a secondary hormone called Insulin-like
Growth Factor (IGF-1), it was imperative to determine whether the concentration
of this secondary action hormone, IGF-1, actually increased after exposure
to HTA5. As the results of figure 2 illustrate,
there is a considerable increase in IGF-1 across all age ranges, with
what appears to be a slightly better response by women. It should be noted
that the greatest percent change in IGF-1 levels was observed in participants
that started with very low baseline IGF-1 concentrations.
Given the increase in IGF-1 levels in the study participants, it was anticipated
that each participant would experience a variety of general health benefits.
And indeed, participants reported an improvement in their exercise stamina,
an increase in the duration of restful sleep, a decrease in the rate of
hair loss, and an impression that their skin was thickening. Other studies
find participants reporting an improvement in their sexual performance
and memory capabilities.
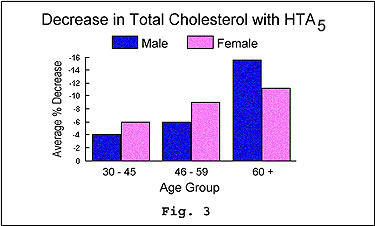
After comparing the before and after blood
samples taken from each participant, a collection of laboratory data was
created that substantiated the efficacy of HTA5
across a number of important parameters. All study participants experienced
a significant absolute decrease in their total cholesterol levels (see
figure 3), regardless of sex.
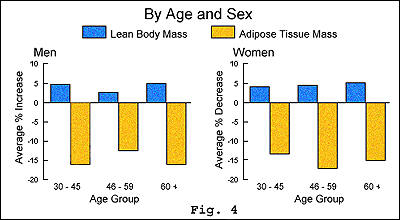
Participants
also experienced an increase in their body's lean muscle mass as measured
by an absolute increase of lean body mass and a considerable decrease
in adipose tissue mass (see figure 4).
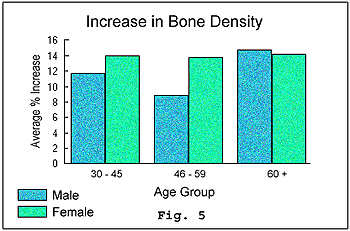
The final
test, which measured for a change in bone density in the arm, also revealed
a favorable increase in the bone density (see figure 5) of participants
regardless of age or sex.
Conclusion:
The study presented above answers our fundamental question regarding the
potential efficacy of an orally administered hGH releasing stimulant in
the form of KeyTropin with HTA5. More importantly,
however, is that the data obtained from blood testing actually suggest
a significant improvement in important physiological parameters such as
total cholesterol and bone density. When put beside the subjective improvement
in well-being reported by the study participants, KeyTropin with HTA5
confirmed its bio-availability with oral administration and its efficacy.

|
|




